Overview
The article titled "7 Key Insights on Collection Debt Statute of Limitations" provides a comprehensive examination of the critical aspects and implications of the statute of limitations concerning debt collection in Canada. It highlights essential insights, including:
- The varying time limits for debt collection across provinces
- The actions that can reset the statute
- The necessity of understanding these legal frameworks to effectively navigate financial recovery
This knowledge is vital for stakeholders aiming to optimize their strategies in debt management.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of debt collection is paramount in today's financial landscape, where both borrowers and lenders navigate a complex web of regulations. This article explores the collection debt statute of limitations in Canada, emphasizing the diverse timeframes across provinces and the significant implications these laws hold for financial recovery efforts.
Many individuals remain unaware of how their actions can reset these time limits, underscoring the necessity for clarity and strategic awareness.
What challenges do borrowers and lenders face in navigating these statutes? How can they effectively manage their obligations while safeguarding their rights?
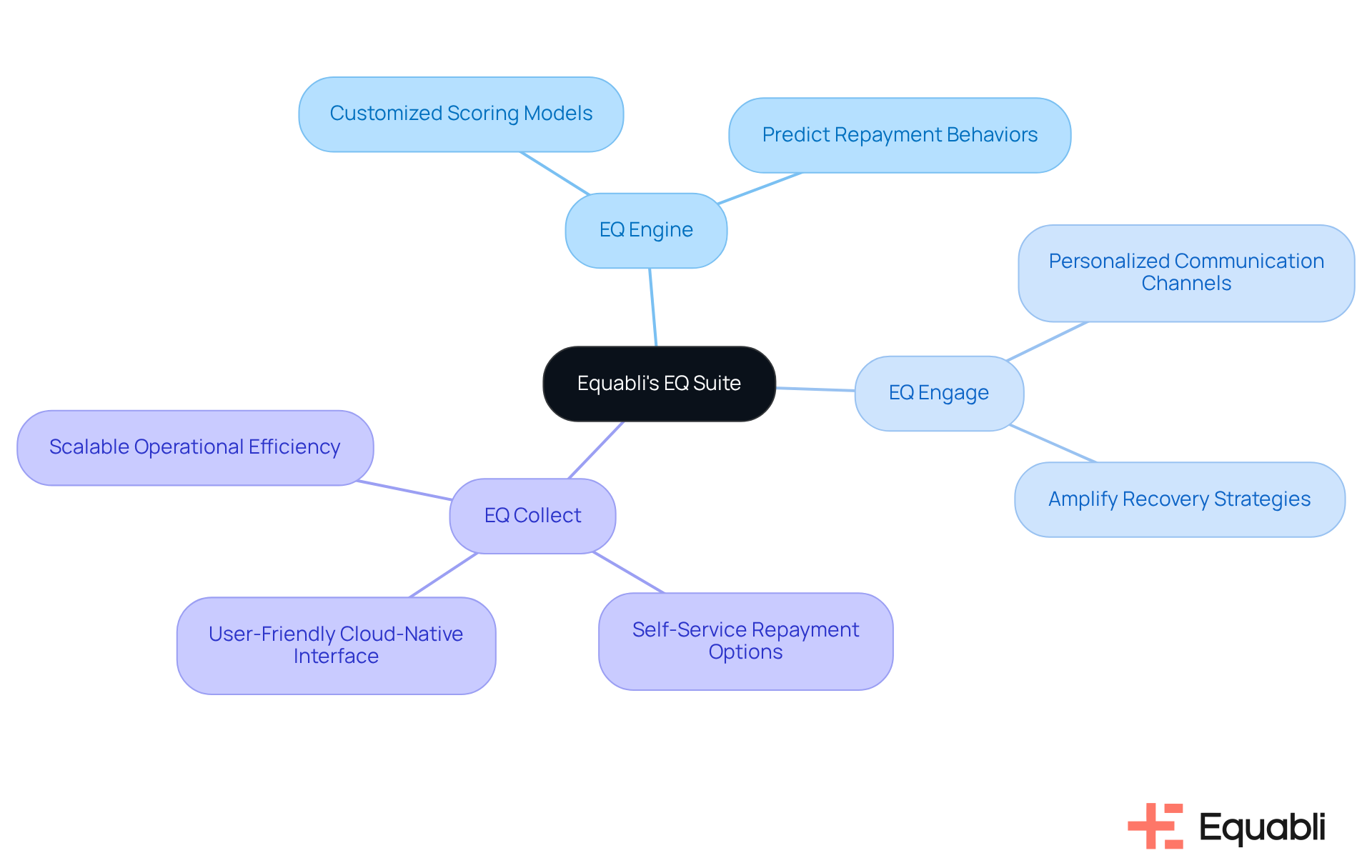
Equabli's EQ Suite: Modern Solutions for Debt Collection Challenges
Equabli's EQ Suite represents a robust array of tools meticulously designed to address the challenges inherent in conventional financial recovery. This suite, which includes the EQ Engine, EQ Engage, and EQ Collect, leverages advanced analytics and automation to enhance operational efficiency.
- The EQ Engine empowers clients to create customized scoring models that predict repayment behaviors.
- EQ Engage amplifies recovery strategies via personalized communication channels.
- Furthermore, EQ Collect facilitates digital assemblies through self-service repayment options, allowing borrowers to manage their obligations on their terms.
- Notably, EQ Collect boasts a user-friendly, scalable, cloud-native interface that significantly enhances operational efficiency.
By embracing these innovative solutions, organizations can markedly reduce retrieval costs, improve borrower engagement, and attain superior compliance and operational efficiency. The integration of cloud-based tools further optimizes processes, enabling real-time data access and informed decision-making—critical elements in today's rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Importantly, Equabli is unwavering in its commitment to safeguarding private information, ensuring that all data handling practices adhere to industry standards for privacy and security.
Statute of Limitations: Time Limits for Debt Collection in Canada
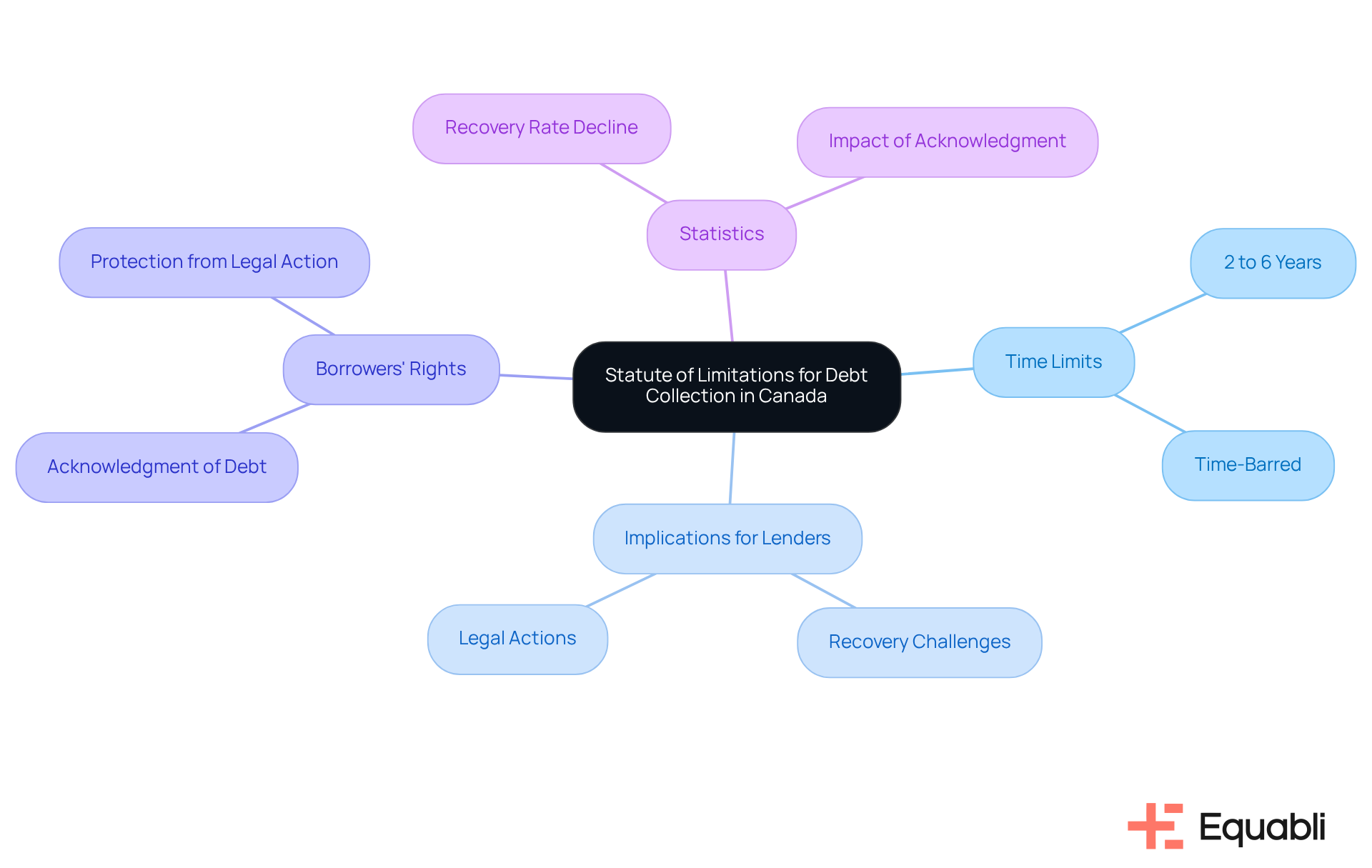
In Canada, the statute of limitations for collecting money varies by province, typically ranging from two to six years. This legal timeframe establishes the duration during which lenders can initiate legal proceedings to recover amounts owed. Once this period expires, the obligation is deemed 'time-barred.' While collectors may still attempt to recover the debt through calls or other methods, they are prohibited from initiating legal action for repayment. Understanding these boundaries is essential for both borrowers and lenders to navigate the complexities of financial recovery effectively.
Statistics reveal that lenders frequently encounter a substantial decline in recovery success rates once the statute of limitations has elapsed. For example, a study indicates that recovery rates can plummet by as much as 50% after the limitation period concludes. Legal experts emphasize that acknowledging an obligation can reset the statute of limitations, thereby extending the timeframe for potential legal action. As highlighted by Hoyes, Michalos & Associates Inc., "If the statute of limitations on an unsecured obligation has expired, lenders won’t have any legal ways to capture your wages or pursue your assets in court." Consequently, it is imperative for both parties to remain informed about current regulations and strategies concerning financial recovery to avoid unnecessary complications and ensure compliance with legal standards.
Provincial Variations: Statute of Limitations Across Canada
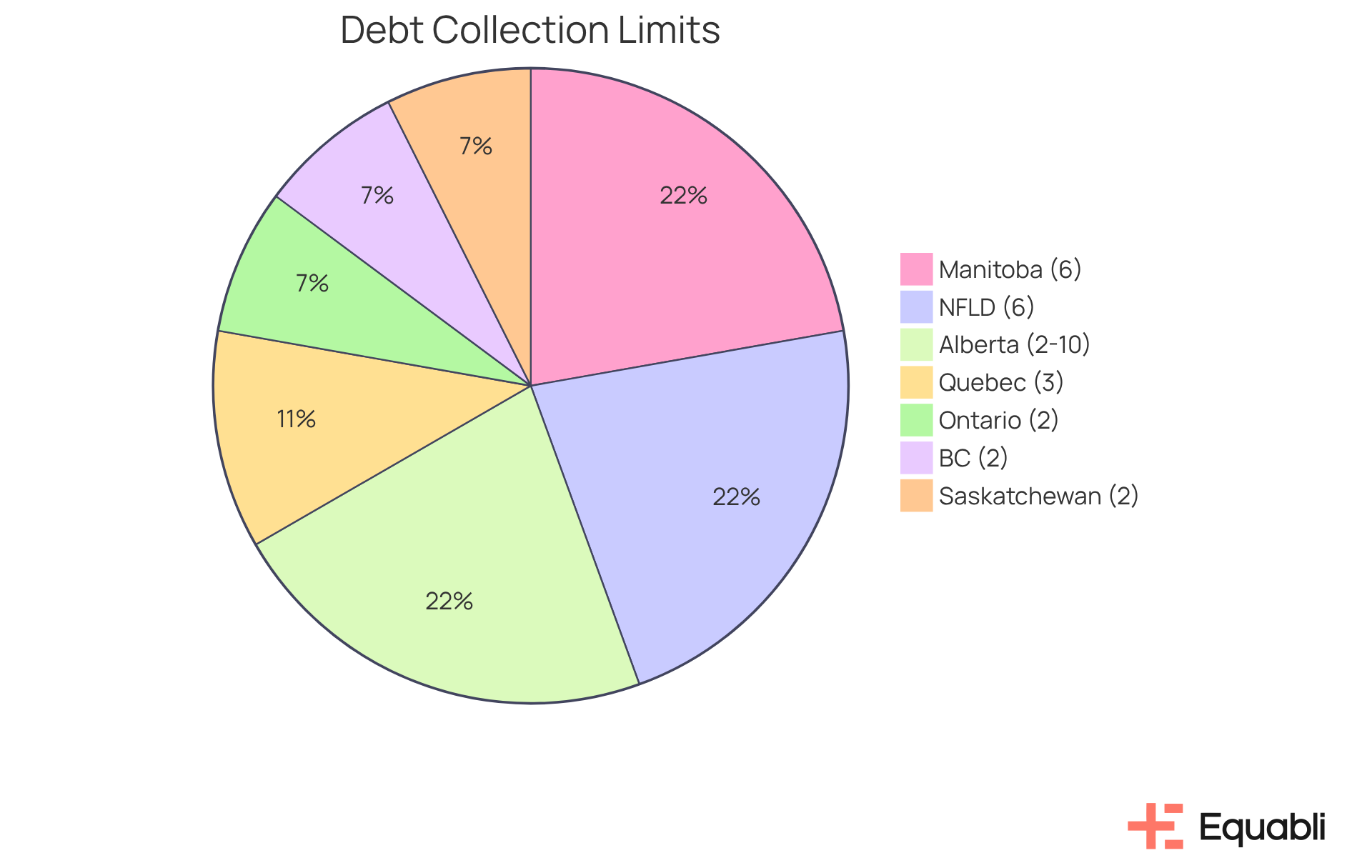
In Canada, the collection debt statute of limitations for collecting amounts owed varies significantly by province, impacting both lenders and borrowers. For instance:
- Ontario enforces a two-year limit.
- Manitoba and Newfoundland and Labrador extend this period to six years.
- British Columbia has a limitation set at two years.
- Quebec allows three years.
Understanding these distinctions is essential, as they dictate the legal measures lenders can pursue and inform the collection debt statute of limitations that debtors may employ to manage their obligations.
In Alberta, the statute ranges from two to ten years, depending on the type of obligation—a crucial detail for lenders to consider. Conversely, Saskatchewan maintains a strict two-year limit. This variability necessitates tailored collection strategies that align with provincial regulations. For example, creditors in regions with extended limitation periods may adopt more assertive recovery tactics, such as increased communication efforts or legal action, knowing they have additional time to pursue claims.
Legal professionals emphasize the importance of understanding the collection debt statute of limitations. As one specialist observed, "Understanding how the statute of limitations on financial obligations in Canada operates may prevent you from a lot of hassle." This insight emphasizes the necessity for both parties to remain cognizant of their rights and responsibilities, ensuring effective management of the complexities involved in collection. It is also crucial to clarify that while liabilities may drop off credit reports after seven years, they do not disappear entirely; lenders can still attempt to collect them.
Resetting the Clock: Actions That Extend the Statute of Limitations
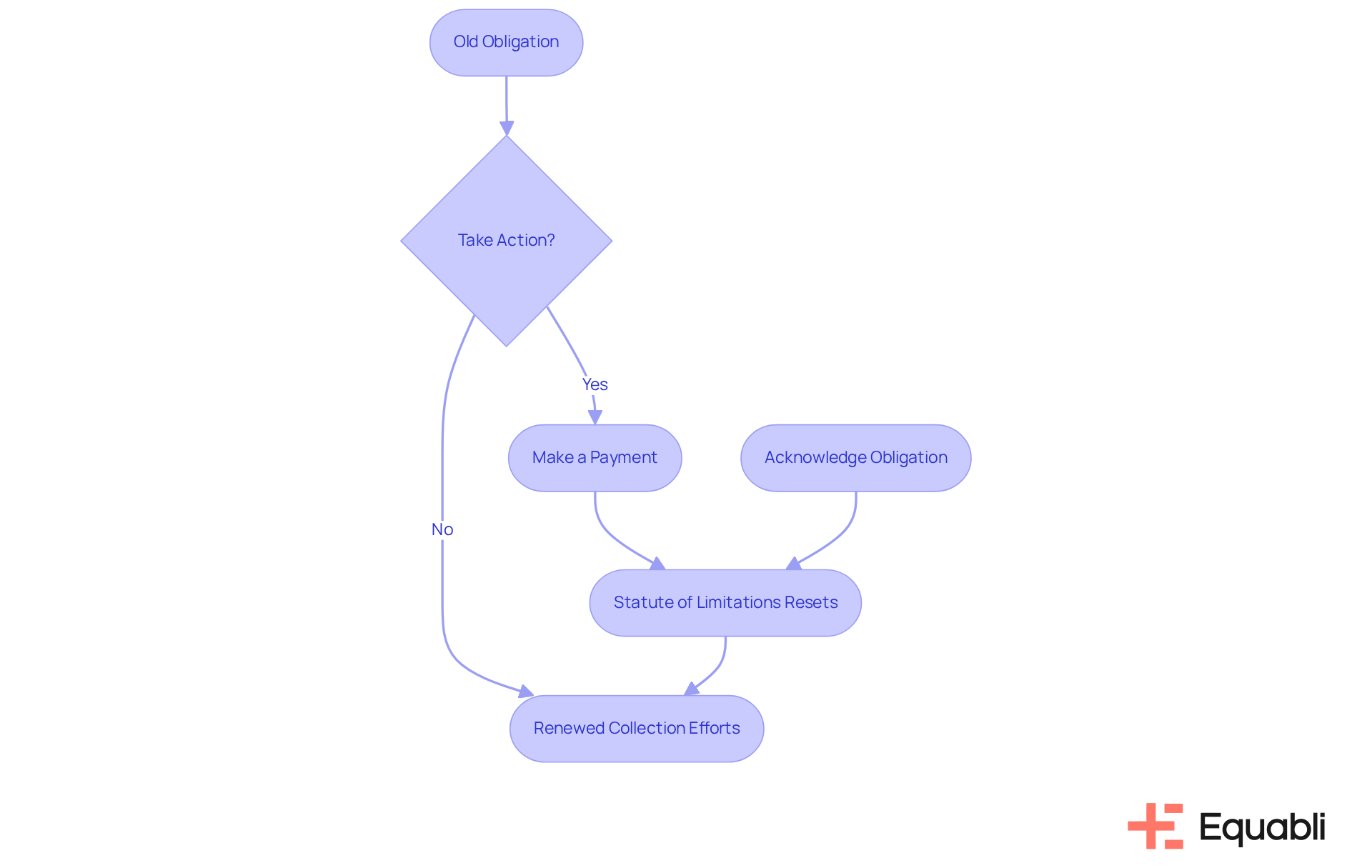
Certain actions can reset the statute of limitations on an obligation, effectively extending the time creditors have to pursue repayment. For instance, making a payment or acknowledging the obligation in writing restarts the clock, potentially leading to unintended consequences for borrowers. This phenomenon, often referred to as 're-aging' financial obligations, can leave individuals vulnerable to renewed collection efforts.
Alarmingly, many borrowers are unaware of how their actions influence the statute of limitations, mistakenly believing that old obligations simply vanish over time. Financial advisors underscore the importance of understanding these dynamics; acknowledging a debt—even in casual conversation—can inadvertently extend the period during which collectors can take legal action.
Legal specialists frequently advise individuals with outstanding debts to refrain from discussing their previous obligations with lenders to avoid re-aging. Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize that adverse information typically remains on a credit report for seven years from the date an obligation first became overdue.
Practical examples illustrate this point: individuals who made partial payments on past obligations found themselves facing renewed recovery efforts, as their actions reset the statute of limitations, enabling creditors to pursue the total amount owed.
To protect themselves from aggressive collection tactics, individuals should remain informed and cautious about communications regarding old obligations and consider consulting with a bankruptcy attorney or requesting written proof of the amount owed before making any payments.
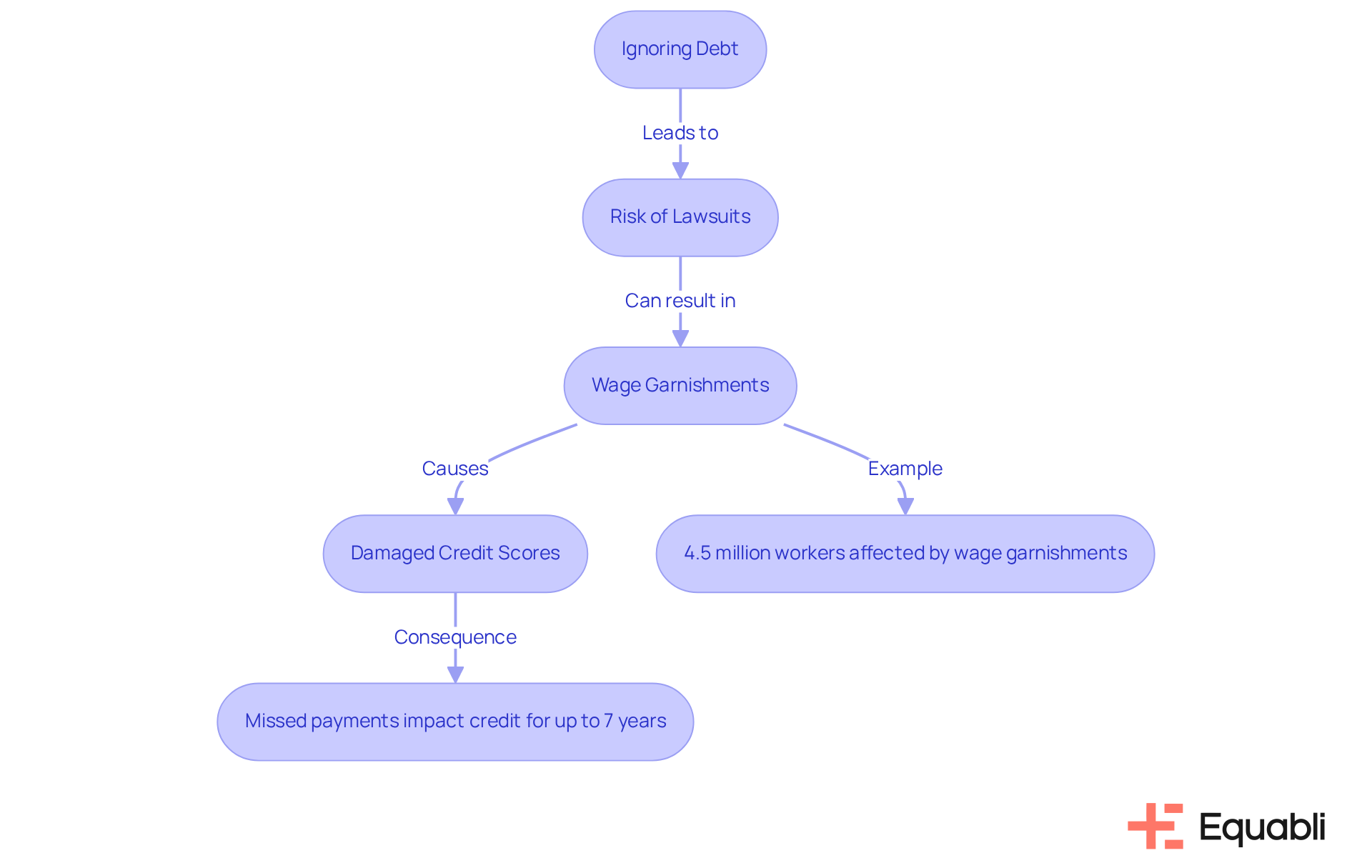
Consequences of Ignoring Debt: Legal and Financial Implications
Neglecting financial obligations can lead to severe legal and financial consequences. Borrowers face the risk of lawsuits, which may result in wage garnishments—an increasingly common outcome, with over 4.5 million workers in the U.S. experiencing wage garnishment for personal loans in 2019 alone. The amount collected through garnishments has surged by approximately 40 percent since 2006, adjusted for inflation, underscoring the escalating severity of this issue. Such actions can significantly damage credit scores, as each missed payment can remain on a report for up to seven years, complicating future loan or mortgage applications.
A notable example is Kevin Evans, who faced substantial wage garnishments after defaulting on a credit card obligation. His experience exemplifies the harsh realities many debtors endure, especially given that state variations in wage garnishment laws can profoundly impact individuals like him. While creditors typically require a court order to garnish wages, exceptions exist for unpaid taxes and child support. Therefore, it is imperative to address liabilities promptly to avert escalating problems that can have enduring effects on financial stability.
Debt Collection Duration: How Long Can Collectors Pursue You?
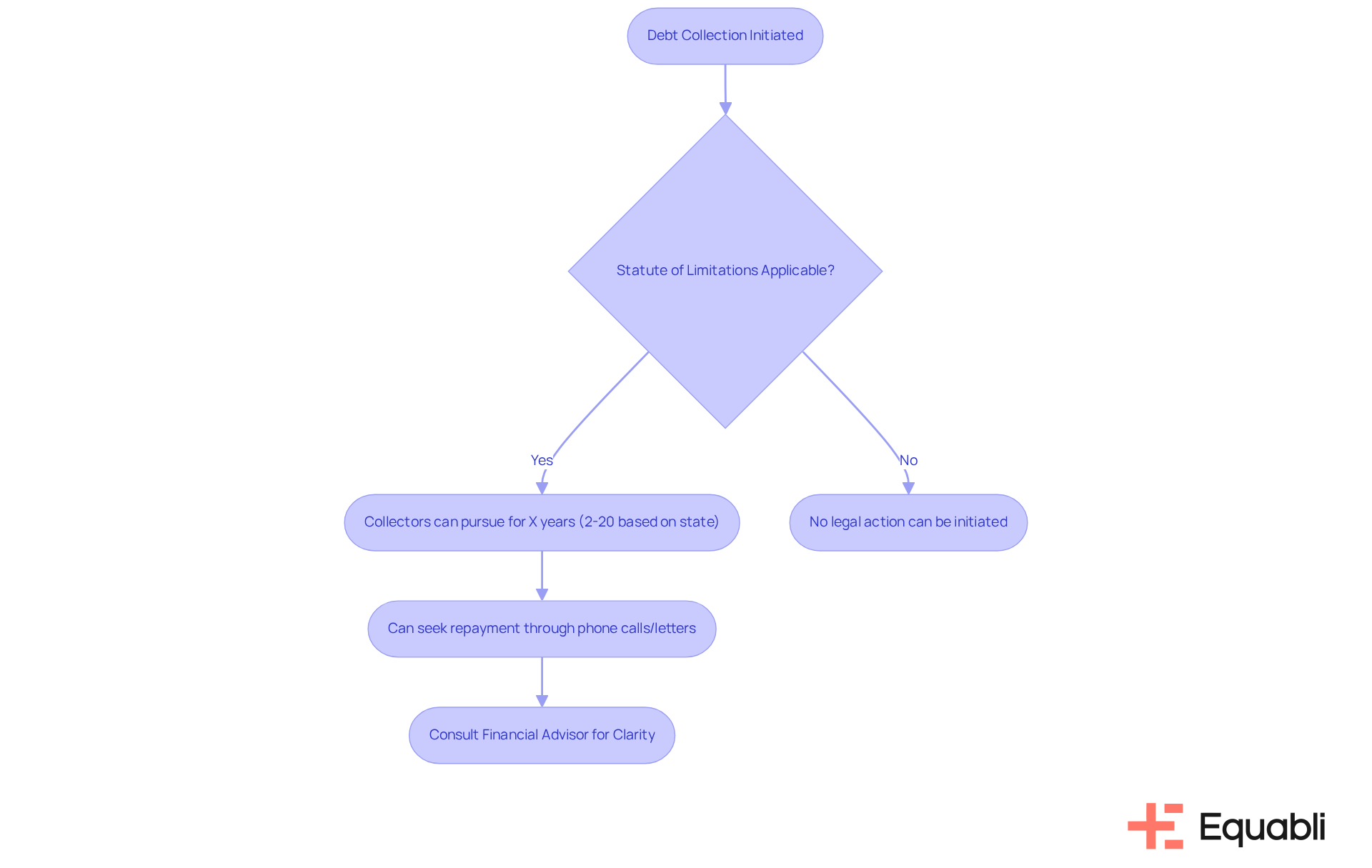
Debt collectors have the ability to pursue repayment indefinitely; however, their capacity to initiate legal action is limited by the statute of limitations. This timeframe varies significantly, spanning from 2 to 20 years depending on the state and the nature of the obligation. Once the statute expires, collectors forfeit the legal right to sue for the debt, although they may still seek to recover through non-legal means, such as phone calls or letters. For instance, in Ontario, creditors are prohibited from commencing court actions related to a card obligation two years after the initial missed payment.
Understanding the collection debt statute of limitations is vital for debtors, as it enables them to effectively manage their financial obligations and recognize their rights. Consumers should be mindful that acknowledging an obligation can reset the statute of limitations clock, which may lead to renewed collection efforts. Furthermore, while collection accounts typically remain on financial reports for seven years, the expiration of the statute does not extinguish the obligation itself. This distinction is essential, as it highlights the ongoing impact of past obligations on credit scoring and overall financial well-being.
Consulting with a financial advisor or consumer attorney can provide clarity on these matters, enabling individuals to make informed decisions regarding their financial responsibilities.
Credit Score Impact: How Debt Collection Affects Your Credit
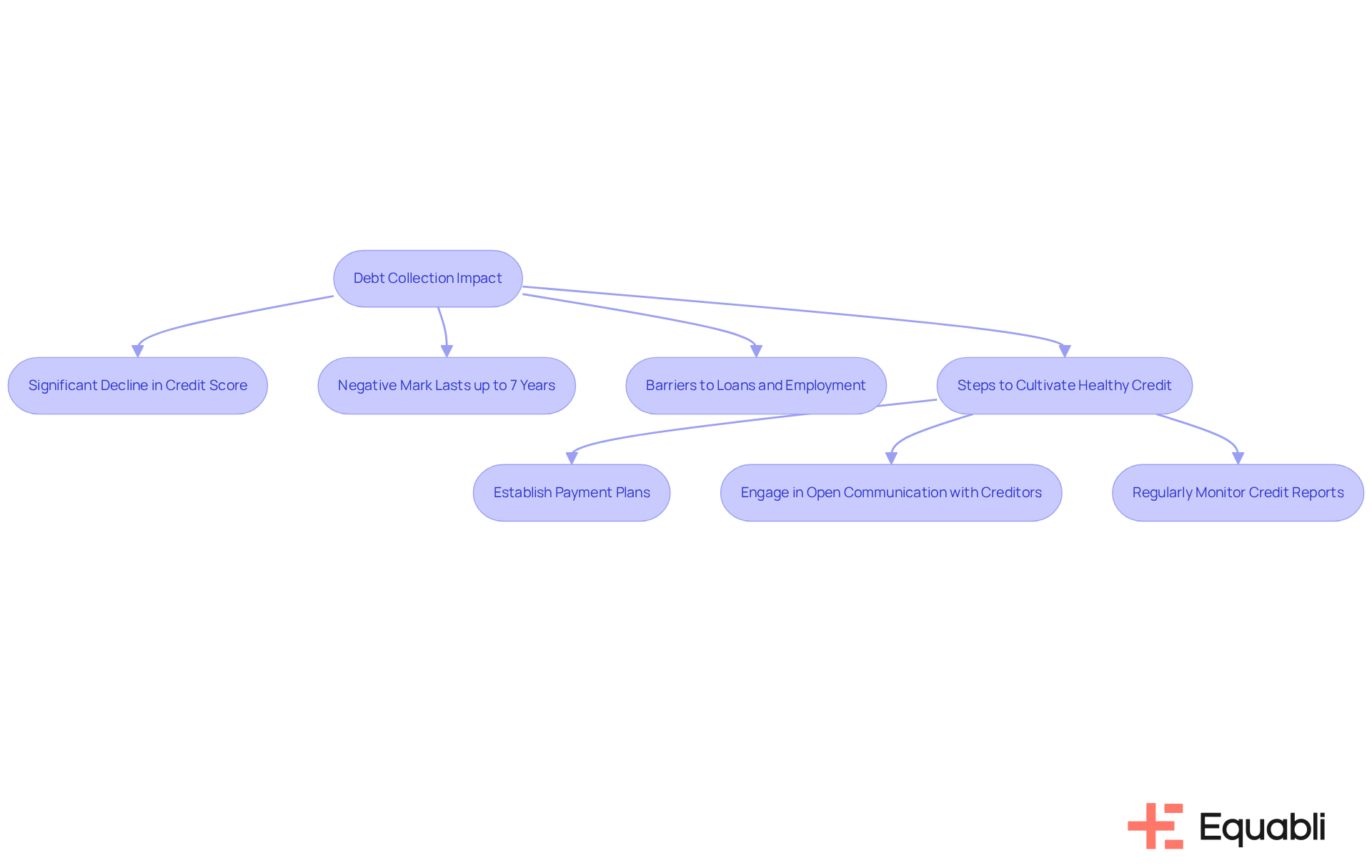
Loan recovery can significantly influence borrowing ratings, with repercussions often lingering long after the original obligation is settled. When an obligation is sent to collections, it is reported to financial agencies, leading to a substantial decline in the borrower's score. This negative mark can persist on a financial report for up to seven years, posing barriers to securing loans, mortgages, or even employment opportunities.
Notably, over 100 million Americans carry medical obligations, underscoring the widespread nature of this issue. A recent study revealed that nearly 70% of medical obligations were removed from consumer financial reports in 2022; however, the remaining outstanding accounts continue to challenge many individuals.
Furthermore, unpaid medical obligations are not reflected on financial reports during the initial year, a modification that could alter the impact of financial recovery on scores. Credit analysts emphasize that the long-term effects of collections can hinder financial mobility, making it essential for individuals to proactively manage their obligations.
To cultivate a healthy credit profile, individuals should consider:
- Establishing payment plans
- Engaging in open communication with creditors
- Regularly monitoring their credit reports for accuracy
Your Rights: Navigating Debt Collection Practices
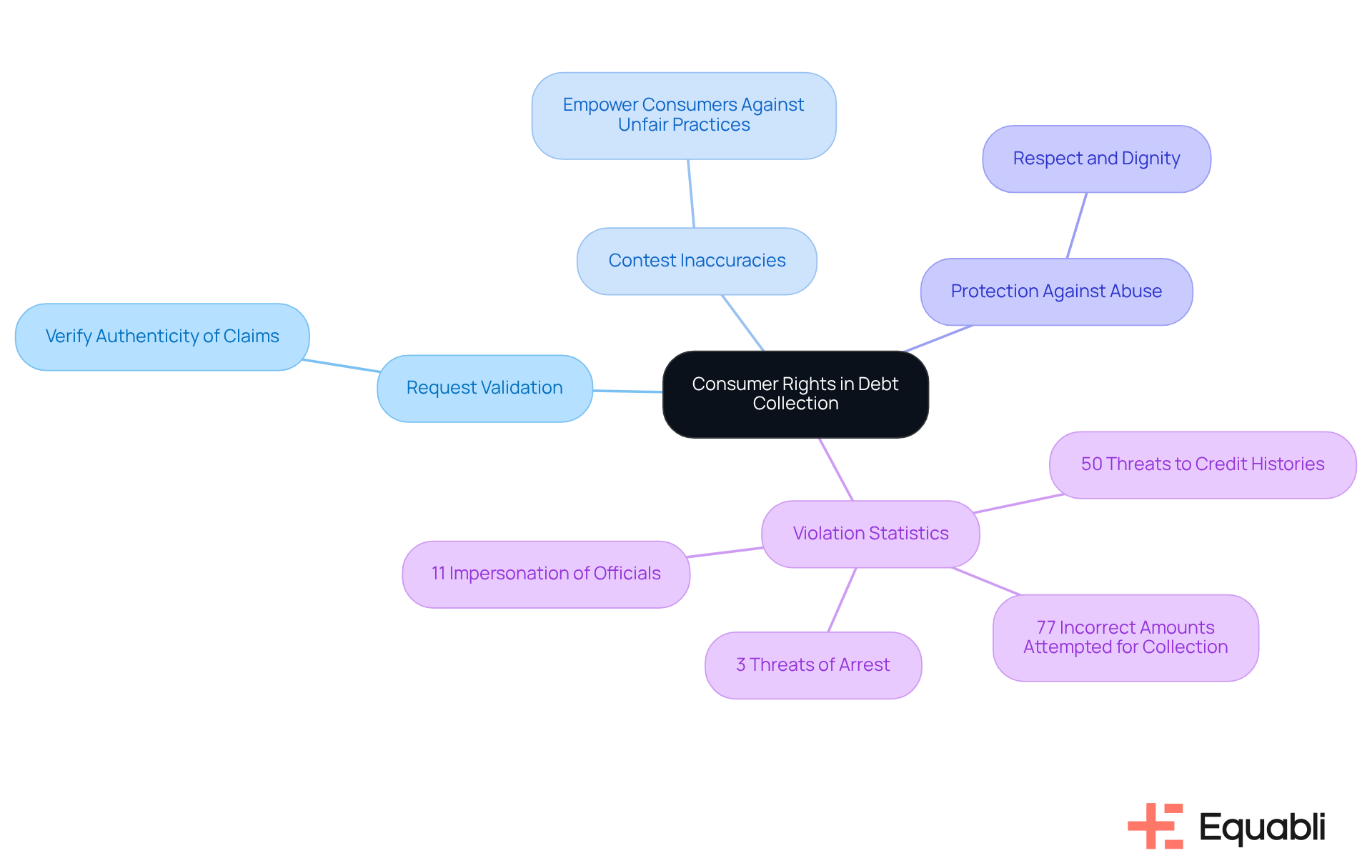
Consumers possess fundamental rights when interacting with collection agents, primarily protected by the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA). This legislation explicitly prohibits abusive, deceptive, or unfair practices, ensuring individuals are treated with respect and dignity. Key rights include:
- The ability to request validation of obligations, allowing consumers to verify the authenticity of claims made against them.
- The right to contest inaccuracies in their financial records, empowering them to effectively confront unfair practices.
Data indicates significant violations of these rights:
- 50% of consumers reported threats to damage their credit histories.
- 77% indicated that collectors attempted to collect incorrect amounts.
These statistics underscore the necessity for consumers to be informed and assertive in their interactions with collection agencies. Legal specialists emphasize that understanding these rights is crucial for individuals to navigate the complexities of financial recovery processes with confidence.
Recent updates to the FDCPA further reinforce consumer protections, highlighting an ongoing commitment to curbing unethical practices within the industry. Successful disputes against unethical financial recovery practices serve as critical examples, demonstrating that consumers can hold collectors accountable for violations. For instance, the FTC's recent actions against GCI and Redon, resulting in a monetary judgment of $9,684,338, illustrate the serious consequences of deceptive practices. By exercising their rights, individuals can mitigate the effects of aggressive collection strategies and work towards settling their obligations on fair terms.
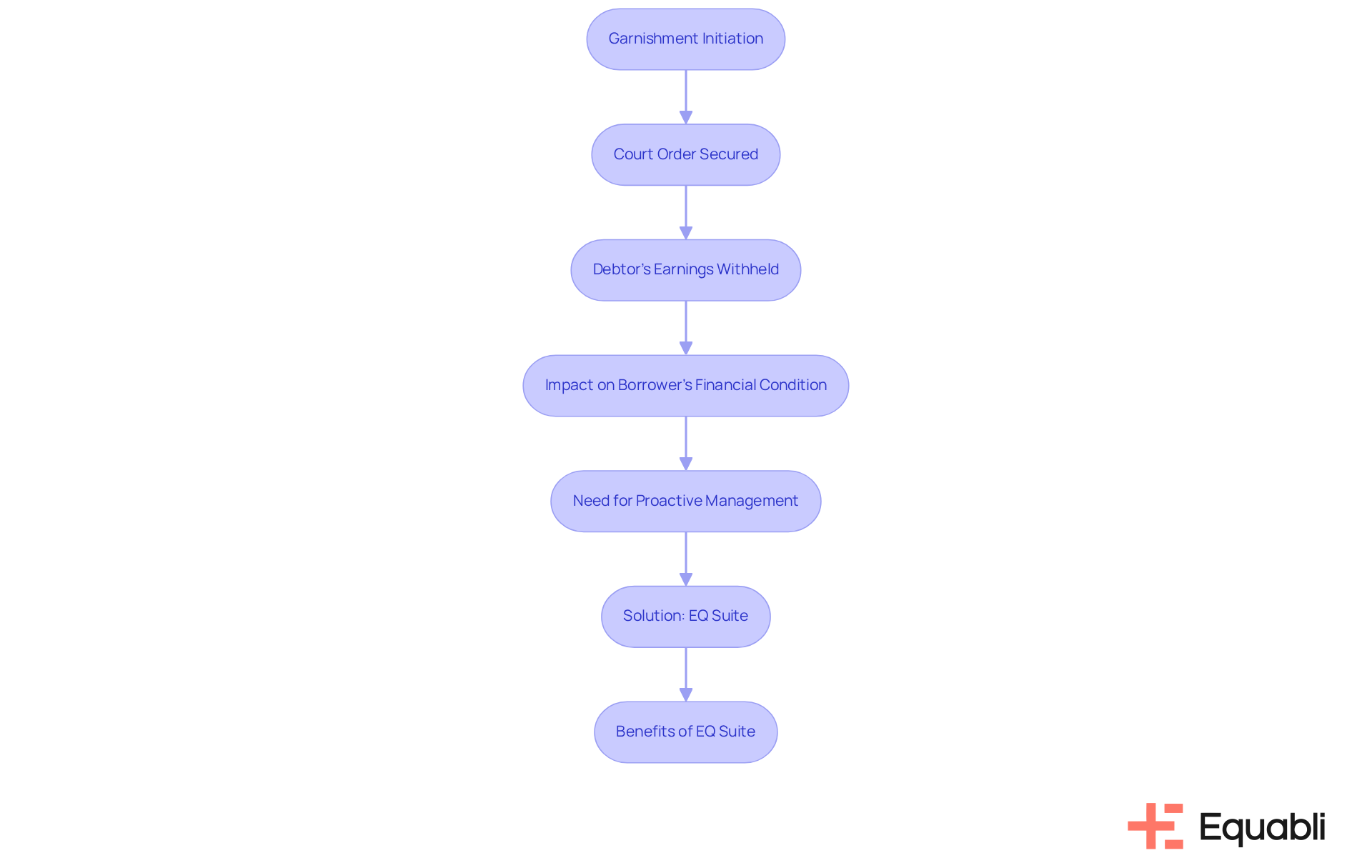
Garnishment Explained: What You Need to Know
Garnishment represents a significant legal procedure that allows lenders to directly retrieve amounts from a debtor's earnings or bank accounts. Once secured by a court order, a portion of the debtor's earnings is withheld and sent to the creditor until the obligation is satisfied. This process can profoundly impact a borrower’s financial condition, underscoring the importance of addressing obligations before they escalate to garnishment. In the realm of manual financial recovery, garnishment is often cumbersome and reactive.
By leveraging Equabli's EQ Suite, financial institutions can modernize their recovery processes, proactively manage obligations, and significantly reduce the likelihood of reaching the garnishment stage. The EQ Suite provides intelligent, cloud-based solutions designed to streamline operations and enhance recovery efforts. This ultimately benefits both creditors and debtors, fostering a more efficient financial ecosystem.
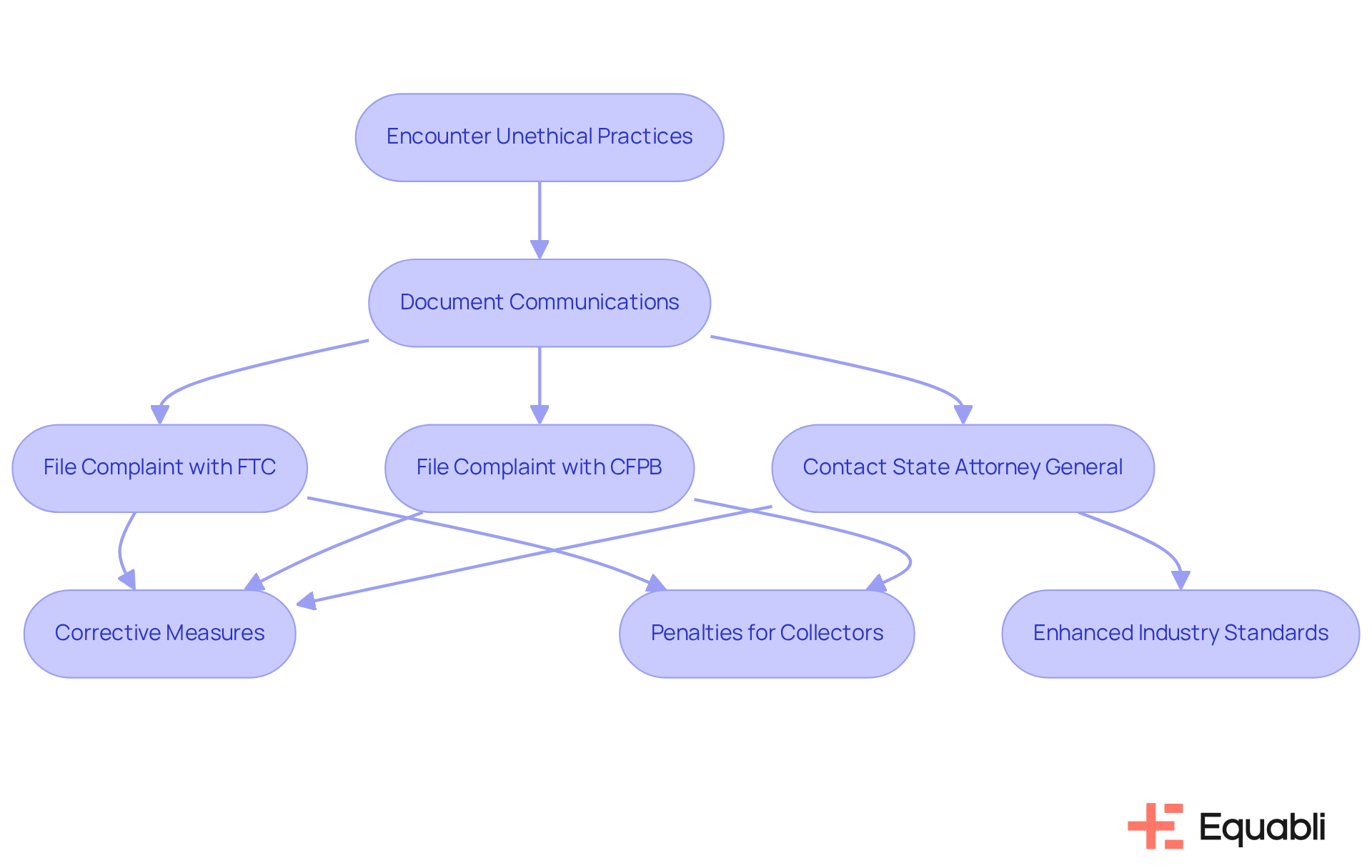
Reporting Violations: How to Address Unethical Debt Collection Practices
Consumers encountering unethical financial collection practices possess the right to report these violations to various regulatory bodies. Complaints can be lodged with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), both of which play crucial roles in enforcing consumer protection laws. Furthermore, state attorneys general can take action against violators, thereby reinforcing consumer rights.
Submitting a complaint serves not only as an individual remedy but also fulfills a broader purpose by holding creditors accountable and contributing to the enhancement of industry standards. Data indicates that approximately 30% of grievances result in corrective measures against collection agencies, underscoring the efficacy of reporting infractions. Successful complaints can lead to substantial penalties for collectors, including statutory damages of up to $1,000 and coverage of attorney's fees for the complainant.
Consumer rights advocates emphasize the importance of documenting all communications with creditors and filing complaints when infractions occur. Christopher Mufarrige, Director of the FTC’s Bureau of Consumer Protection, asserts, "Utilizing a strategy of intimidation and threats of imprisonment to force consumers into making payments that they don’t owe is unacceptable." This proactive approach not only safeguards individual rights but also cultivates a more ethical debt collection environment. By standing against abusive practices, consumers can drive systemic change within the industry.
Conclusion
Understanding the statute of limitations for debt collection is essential for both lenders and borrowers navigating the complexities of financial recovery. This article illuminates the varying time limits across Canada, underscoring the importance of being informed about one's rights and obligations. By comprehending these legal frameworks, individuals can effectively manage their debts and avert unnecessary complications.
Key insights reveal the diverse provincial regulations that dictate the duration for initiating legal actions, the implications of resetting the statute of limitations, and the potential consequences of ignoring debt. Moreover, the article emphasizes the significance of leveraging modern solutions like Equabli's EQ Suite, which enhances operational efficiency and borrower engagement throughout the debt collection process.
Ultimately, staying informed about debt collection laws and understanding one’s rights is vital in today’s financial landscape. Individuals are encouraged to proactively manage their financial obligations, consult with professionals when necessary, and report any unethical practices they encounter. By doing so, they can protect their financial well-being and contribute to a more equitable debt collection environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Equabli's EQ Suite?
Equabli's EQ Suite is a collection of tools designed to tackle challenges in financial recovery, including the EQ Engine, EQ Engage, and EQ Collect, which utilize advanced analytics and automation to improve operational efficiency.
How does the EQ Engine function?
The EQ Engine allows clients to create customized scoring models that predict repayment behaviors, helping organizations tailor their recovery strategies.
What role does EQ Engage play in the debt collection process?
EQ Engage enhances recovery strategies by utilizing personalized communication channels to engage borrowers more effectively.
What features does EQ Collect offer?
EQ Collect provides digital assemblies through self-service repayment options, allowing borrowers to manage their obligations on their terms, and features a user-friendly, scalable, cloud-native interface.
What benefits do organizations experience by using Equabli's solutions?
Organizations can reduce retrieval costs, improve borrower engagement, and achieve better compliance and operational efficiency by adopting these innovative tools.
How does the integration of cloud-based tools benefit financial recovery processes?
Cloud-based tools optimize processes by enabling real-time data access and informed decision-making, which are crucial in the fast-changing financial environment.
What measures does Equabli take to protect private information?
Equabli is committed to safeguarding private information and ensures that all data handling practices comply with industry standards for privacy and security.
What is the statute of limitations for debt collection in Canada?
The statute of limitations for collecting debts in Canada varies by province, typically ranging from two to six years, establishing the period during which legal action can be initiated.
What happens once the statute of limitations expires?
Once the statute of limitations expires, the obligation is considered 'time-barred,' meaning lenders cannot initiate legal action to recover the debt, although they may still attempt to collect it through other means.
How does acknowledging an obligation affect the statute of limitations?
Acknowledging an obligation can reset the statute of limitations, extending the timeframe during which lenders can pursue legal action for repayment.
What are the specific statute of limitations for different provinces in Canada?
In Canada, the statute of limitations varies by province: Ontario has a two-year limit, Manitoba and Newfoundland and Labrador have six years, British Columbia has two years, Quebec has three years, and Alberta ranges from two to ten years depending on the type of obligation.
Why is it important for both borrowers and lenders to understand the statute of limitations?
Understanding the statute of limitations is essential for both parties to navigate financial recovery effectively, avoid unnecessary complications, and ensure compliance with legal standards.




