Overview
Navigating a Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) complaint requires a comprehensive understanding of consumer rights and the necessary steps to take action. Begin by gathering essential documentation, which is crucial for an effective complaint. This article delineates critical steps:
- Compile personal and agency information
- Detail the obligation
- Maintain thorough records
Such preparation empowers consumers to advocate effectively for their rights against unfair collection practices, ensuring they are well-equipped to confront challenges in the debt collection landscape.
Introduction
The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) stands as a vital safeguard for consumers, specifically crafted to counter the often formidable tactics employed by debt collectors. This comprehensive guide explores the complexities of filing a complaint under the FDCPA, empowering individuals with the essential knowledge required to navigate the grievance process effectively. As the landscape of debt collection practices evolves and potential legislative changes loom, how can consumers guarantee that their rights are upheld and their voices resonate within a system that may appear intimidating?
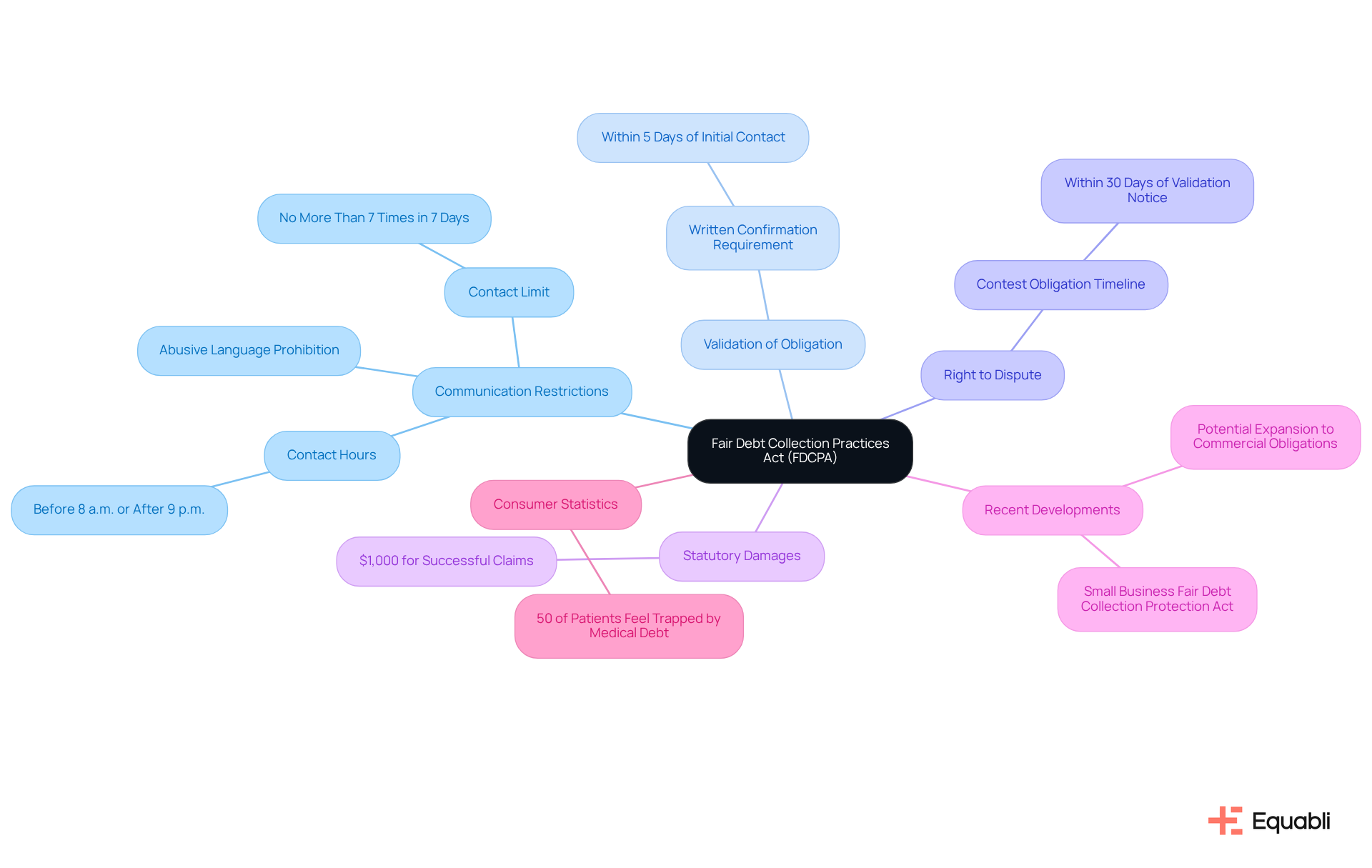
Understand the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA)
The Fair Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) stands as a pivotal federal statute aimed at curbing abusive, deceptive, and unfair collection practices. Established in 1977, it seeks to protect consumers from harassment while delineating permissible actions for collection agencies. Key provisions of the FDCPA include:
- Communication Restrictions: Debt collectors are prohibited from contacting consumers at unreasonable hours, specifically before 8 a.m. or after 9 p.m., and must avoid using abusive language during communications. Furthermore, collectors cannot reach out to a consumer regarding their obligation more than seven times within a seven-day period.
- Validation of Obligation: Collectors are mandated to provide written confirmation of the obligation within five days of initial contact, ensuring transparency throughout the collection process.
- Right to Dispute: Consumers possess the right to contest the obligation within 30 days of receiving the validation notice, empowering them to challenge the legitimacy of the claim.
Statutory damages under the FDCPA can amount to $1,000 for successful claims against non-compliant creditors, highlighting the financial repercussions of violations. Recent developments indicate a potential extension of the FDCPA to cover commercial obligations, which may introduce new compliance challenges and litigation risks for businesses. The proposed aims to offer similar protections to small business owners, reflecting a growing recognition of the need for fair treatment in financial recovery practices.
Statistics reveal that nearly 50% of patients facing medical financial burdens feel trapped, underscoring the FDCPA's vital role in safeguarding consumer rights. Additionally, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) has prioritized regulations addressing harmful recovery practices, particularly concerning medical debts, illustrating the FDCPA's ongoing evolution in response to contemporary challenges. CFPB Director Rohit Chopra emphasized that protecting law-abiding creditors from unlawful practices is crucial for maintaining a fair marketplace.
Legal experts assert that understanding these rights is essential for individuals effectively navigating the grievance process when filing a fair debt collection practices act complaint. As the landscape of financial recovery continues to evolve, staying informed about the FDCPA's regulations and impending changes is imperative for both consumers and recovery agencies.
Gather Necessary Information for Your Complaint
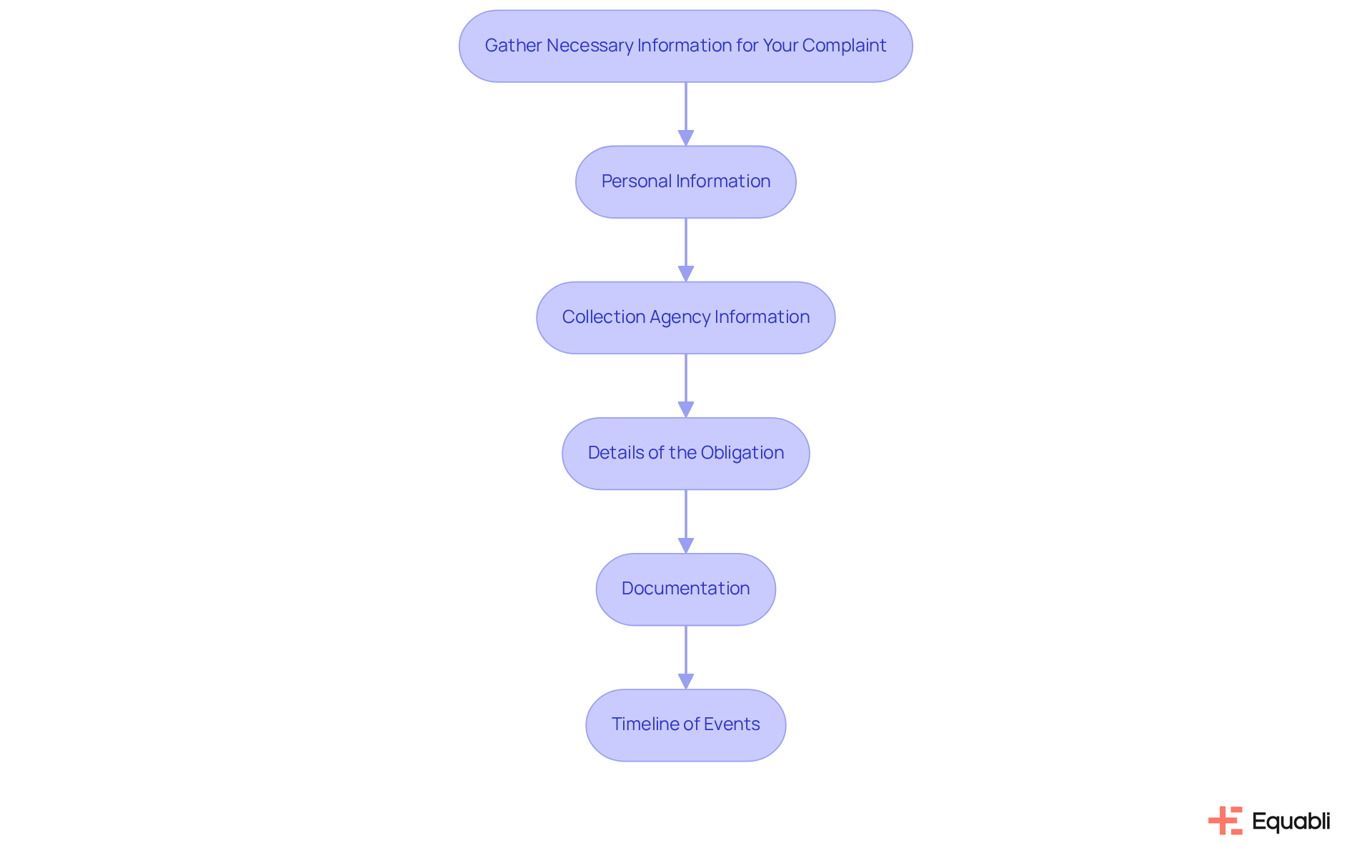
To file a effectively, it is essential to gather comprehensive information that supports your case. Start by compiling the following key elements:
- Personal Information: Your full name, address, and contact details are crucial to establish your identity.
- Collection Agency Information: Record the name of the collection agency, their contact details, and the names of any representatives you engaged with.
- Details of the Obligation: Clearly outline the amount owed, the original creditor, and any relevant account numbers associated with the obligation.
- Documentation: Gather all communication with the collector, such as letters, emails, and notes from phone calls. This documentation serves as critical evidence of any violations and supports your claims.
- Timeline of Events: Create a detailed timeline of your interactions with the creditor, noting specific dates and details of each communication. This structured account clarifies the sequence of events in your concern and strengthens your position.
In 2025, the FTC indicated more than 112,000 grievances related to financial recovery, emphasizing the significance of being adequately prepared when submitting your own fair debt collection practices act complaint. Effective resolutions frequently arise from comprehensive documentation and transparent communication, as highlighted by consumer rights lawyers who support consumers in understanding their rights and the correct processes for submitting grievances. By following these steps, you can enhance your chances of a favorable outcome.
File Your Complaint with the Appropriate Authorities
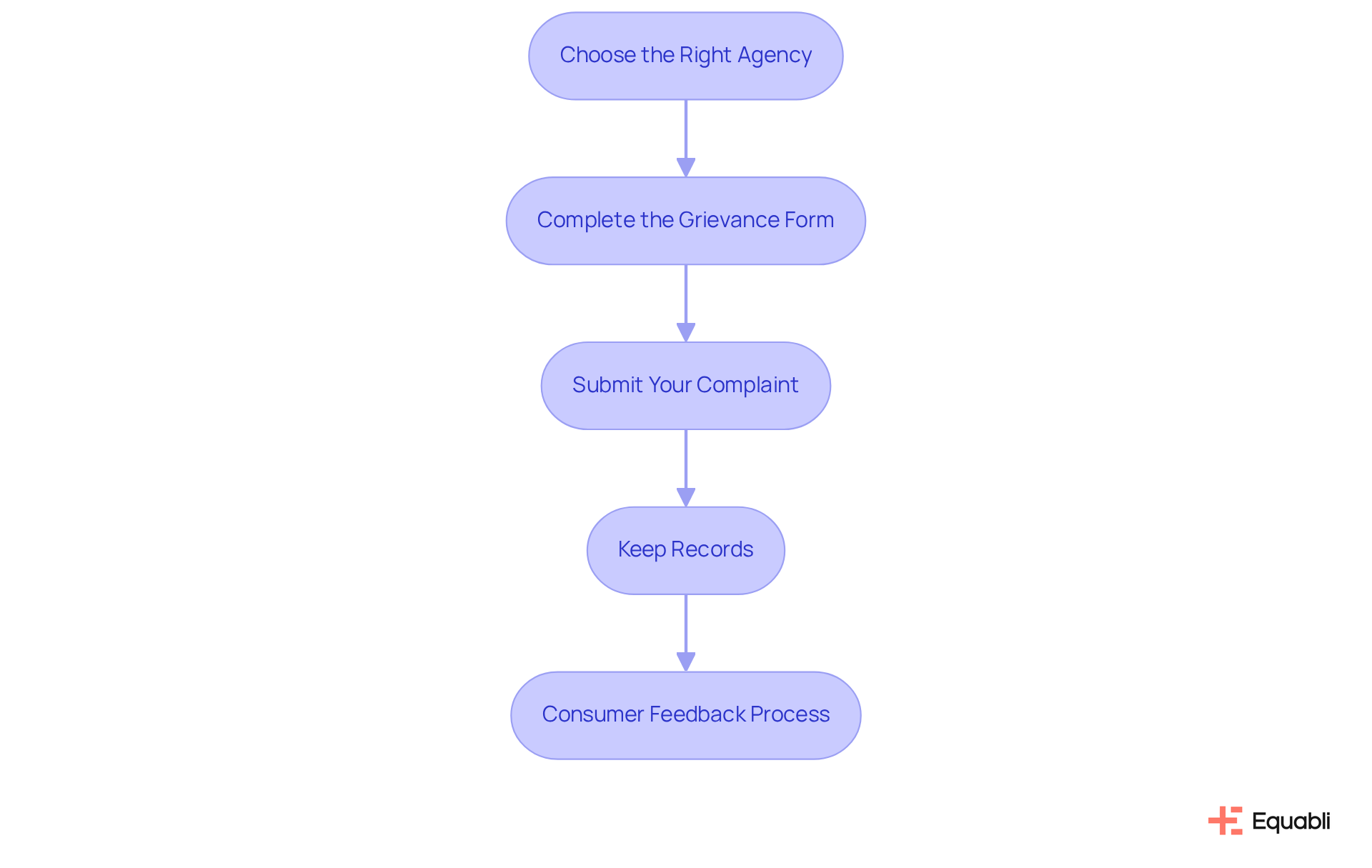
To effectively file your complaint regarding debt collection practices, follow these steps:
-
Choose the Right Agency: Depending on the specifics of your complaint, you can file with:
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) for general debt collection issues.
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) for issues related to consumer financial products and services.
- Your state's attorney general for violations specific to your state.
-
Complete the Grievance Form: Access the agency's website and fill out the grievance form. Ensure you provide detailed information, including clear descriptions, relevant dates, and supporting documents to strengthen your case. If submitting for someone else, written authorization is generally required.
-
Submit Your Complaint: Follow the agency's submission guidelines, which may include options for online submission, mailing, or phone calls. Submitting a grievance online usually requires under 10 minutes. You will need to provide your contact information to create a secure account for submitting a grievance.
-
Keep Records: Maintain copies of your grievance and any correspondence with the agency for your records. This documentation is essential for monitoring the progress of your issue and for any possible follow-up actions.
In 2025, the CFPB reported that over 50,000 grievances regarding financial products and services are sent to companies weekly, highlighting the significance of consumer feedback in identifying marketplace issues. Companies generally address grievances regarding a fair debt collection practices act complaint within 15 days, with a final reply possible within 60 days. If a grievance cannot be sent to a company, it may be forwarded to another federal agency. Customers will be informed when a company replies to their concern and have 60 days to give feedback. This process not only but also helps improve industry practices. Remember, if you suspect fraudulent activity, report it to local authorities or the FTC to ensure swift action.
Follow Up and Understand the Next Steps
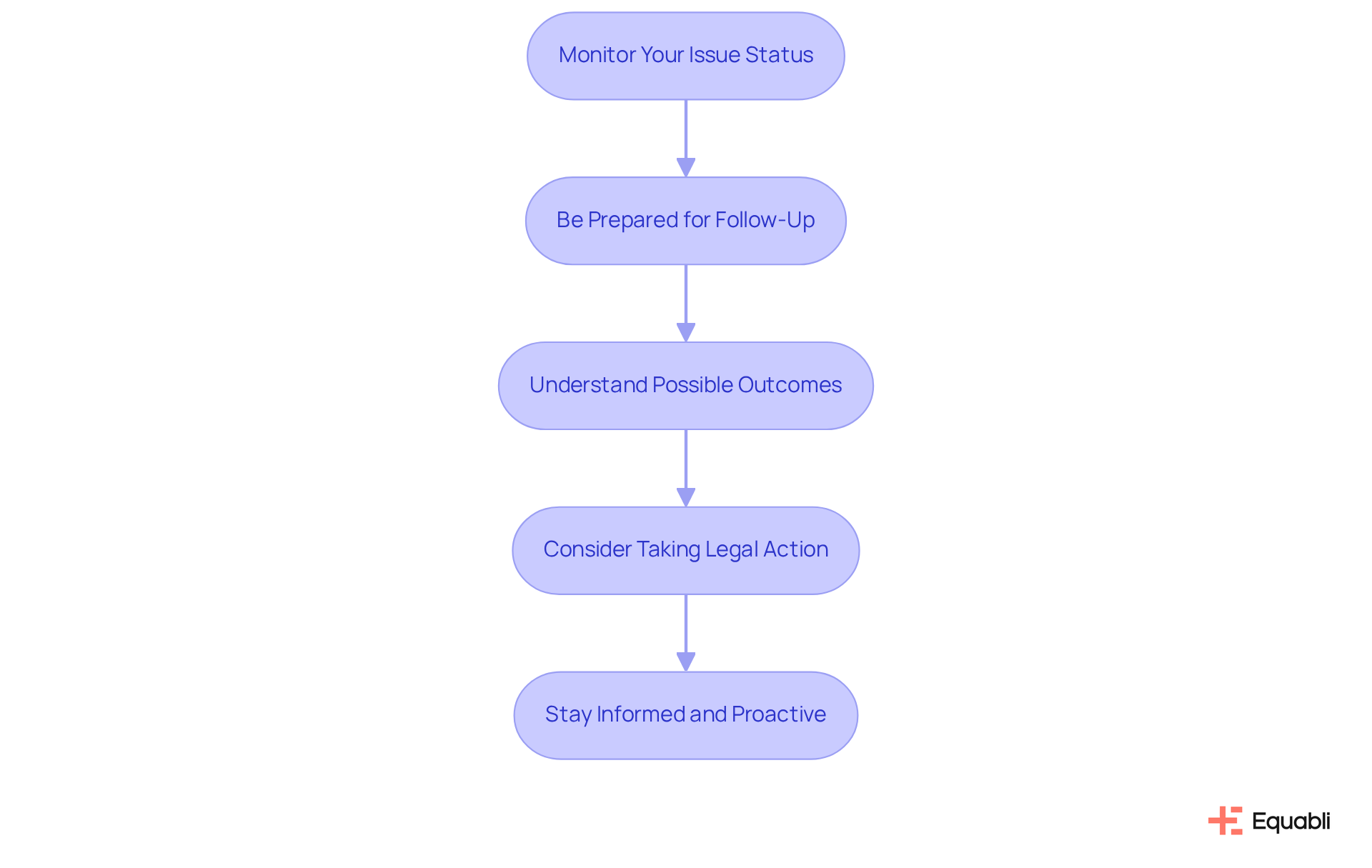
After filing your complaint, it is crucial to follow these essential steps to ensure effective resolution:
- Monitor Your Issue Status: Regularly check the agency's website or contact them directly to track the status of your concern. Many agencies offer tracking options for your convenience.
- Be Prepared for Follow-Up: Expect to be contacted for further information or clarification. Responding promptly to any inquiries can facilitate the investigation process.
- Understand Possible Outcomes: The agency may opt to examine your concern, mediate between you and the collector, or take if violations are identified. Keep in mind that outcomes can differ significantly based on the details of your issue. As stated by the FTC, more than $20 billion in debt has been settled since 2002, emphasizing the potential effect of the grievance process.
- Consider taking legal action by filing a fair debt collection practices act complaint: If your issue remains unresolved, consulting with a lawyer about potential legal action under the FDCPA may be necessary. Remember, you typically have one year from the date of the violation to initiate a lawsuit.
Consumer advocates highlight the significance of grasping these steps to navigate through the grievance process effectively. As specialists emphasize, "Consumers ought to be informed of their rights under the Fair Collection Practices Act (FDCPA), which forbids collectors from employing abusive, threatening, or harassing tactics." Outcomes from debt collection complaint investigations can vary widely, with some leading to significant resolutions, while others may require further legal intervention. Staying informed and proactive is key to achieving a favorable outcome.
Conclusion
The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) is an essential legal framework designed to protect consumers from unethical debt collection practices. Understanding the rights and protections afforded under this act enables individuals to navigate the often complex landscape of debt collection complaints effectively. The importance of being informed about these regulations cannot be overstated; it empowers consumers to take decisive action against violations that may occur.
This article highlights key provisions of the FDCPA, including:
- Communication restrictions
- The requirement for validation of obligations
- The consumer's right to dispute claims
Furthermore, it meticulously outlines the necessary steps to gather information, file a complaint, and follow up on its status. These insights illustrate the process of asserting consumer rights and the potential outcomes of lodging a complaint, underscoring the significance of thorough documentation and proactive engagement.
Ultimately, understanding and utilizing the FDCPA is crucial for anyone facing debt collection issues. It is not merely about knowing your rights; it is about taking action to ensure those rights are upheld. By staying informed and prepared, consumers can effectively challenge abusive practices and contribute to a fairer financial marketplace. Taking the first step in filing a complaint can lead to significant changes, both personally and within the broader context of consumer protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA)?
The FDCPA is a federal statute established in 1977 aimed at preventing abusive, deceptive, and unfair debt collection practices, thereby protecting consumers from harassment.
What are the communication restrictions placed on debt collectors by the FDCPA?
Debt collectors are prohibited from contacting consumers before 8 a.m. or after 9 p.m., must avoid using abusive language, and cannot contact a consumer more than seven times within a seven-day period regarding their obligation.
What is the validation of obligation requirement under the FDCPA?
Collectors must provide written confirmation of the debt obligation within five days of initial contact, ensuring transparency in the collection process.
Do consumers have the right to dispute debt obligations under the FDCPA?
Yes, consumers have the right to contest the validity of the obligation within 30 days of receiving the validation notice.
What are the potential damages for violations of the FDCPA?
Statutory damages under the FDCPA can amount to $1,000 for successful claims against creditors that do not comply with the Act.
Is there a proposal to extend the FDCPA to cover commercial obligations?
Yes, there are recent developments suggesting a potential extension of the FDCPA to include commercial obligations, which may introduce new compliance challenges for businesses.
What is the Small Business Fair Financial Recovery Protection Act?
This proposed act aims to provide similar protections to small business owners as those afforded to consumers under the FDCPA, highlighting the need for fair treatment in financial recovery practices.
What statistics highlight the importance of the FDCPA?
Nearly 50% of patients facing medical financial burdens feel trapped, emphasizing the FDCPA's role in safeguarding consumer rights.
How is the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) involved with the FDCPA?
The CFPB has prioritized regulations to address harmful recovery practices, especially concerning medical debts, reflecting the FDCPA's ongoing evolution to meet contemporary challenges.
Why is it important for consumers to understand their rights under the FDCPA?
Understanding these rights is essential for effectively navigating the grievance process when filing a complaint regarding debt collection practices.




